The back of the knee, or the popliteal region, is a complex area where several key structures come together. These include the hamstring tendons, the popliteus muscle, the popliteal artery, and nerves like the tibial nerve. When any of these structures become injured or inflamed, it can lead to pain that varies in intensity and impact.
Symptoms of back of knee pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, depending on the cause. You might notice swelling, stiffness, or even a weird popping sound. Sometimes the pain is constant, while other times it only bothers you when you move a certain way. With so many possibilities, figuring out exactly what’s going on is key to finding the right treatment. Let’s dive into the common culprits behind back of knee pain and how to tackle them.
Common Causes of Back of Knee Pain

There are several reasons why someone might experience pain at the back of their knee. Understanding these causes can help in finding the most effective treatment. Here are some of the most common causes:
Overuse Injuries
Overuse injuries are a frequent cause of back of knee pain, especially for athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive activities. These injuries occur when a muscle or tendon is strained due to excessive or repeated use, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Hamstring Strains: The hamstrings are a group of muscles located at the back of your thigh, and they are crucial for bending the knee and extending the hip. When these muscles are overstretched or torn, it can lead to significant pain behind the knee. This type of injury is common in activities that involve sudden starts and stops, like sprinting or playing soccer.
- Popliteus Tendonitis: The popliteus is a small muscle located at the back of the knee, and it plays a key role in unlocking the knee from a fully straightened position. Overuse of this muscle can lead to inflammation of the popliteus tendon, resulting in pain at the back of the knee, especially when walking downhill or descending stairs.
- Baker’s Cyst: Also known as a popliteal cyst, this condition occurs when excess joint fluid collects in the back of the knee, leading to swelling and discomfort. It is often associated with knee problems like arthritis or a meniscus tear. Although the cyst itself is not always painful, it can cause discomfort and restrict movement, particularly when it becomes large.
Arthritis
Arthritis is another common cause of back of knee pain, particularly in older adults. It involves the inflammation of one or more joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common form of arthritis, where the cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones gradually wears away. In the knee, this can lead to bone-on-bone contact, causing significant pain and discomfort, not only in the front but also in the back of the knee. Osteoarthritis often develops over time due to age, overuse, or previous injuries.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joint linings. This can lead to inflammation, swelling, and pain in the knee, including the area behind it. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect people of any age and often involves multiple joints.
Medical Conditions
Other medical conditions can also lead to pain at the back of the knee. These are often less common but can be serious if not addressed promptly.
- Venous Insufficiency: This condition occurs when the veins in the legs have difficulty sending blood back to the heart. As a result, blood pools in the veins, leading to swelling, aching, and sometimes pain at the back of the knee. This is often accompanied by visible varicose veins and a feeling of heaviness in the legs.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. This can cause sudden, severe pain at the back of the knee, along with swelling and redness. DVT requires immediate medical attention, as the clot can travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
- Nerve-Related Issues: Conditions like sciatica, where the sciatic nerve is compressed or irritated, can cause radiating pain that travels down the leg, sometimes affecting the back of the knee. This pain is often sharp and may be accompanied by tingling or numbness.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Back of Knee Pain
Knowing when to see a doctor for back of knee pain is important for getting timely and effective treatment. While some knee pain can be managed at home with rest and care, certain symptoms indicate that it’s time to seek professional help.
If you experience severe pain that prevents you from walking or bearing weight on your leg, you should consult a healthcare provider immediately. Swelling that doesn’t improve with rest, visible deformity, or a popping sound at the time of injury are also red flags. Additionally, if you notice any symptoms of DVT, such as sudden pain, swelling, or redness, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and lead to better outcomes.
Top Non-Surgical Back of Knee Pain Treatments
For many people, non-surgical treatments are effective in relieving back of knee pain and restoring function. These treatments vary depending on the cause of the pain, and a personalized approach is often the most beneficial.
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE)
The RICE method is one of the most common approaches to treating knee pain, particularly for minor injuries like sprains or strains. Resting the knee allows the injured tissue time to heal without further strain. Applying ice helps reduce swelling and numb the area, providing pain relief. Compression, typically with an elastic bandage, helps control swelling, while elevating the leg above heart level reduces blood flow to the area, further decreasing swelling.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the non-surgical treatment of knee pain. A physical therapist can develop a tailored exercise program designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. Therapy often includes a combination of stretching, strengthening exercises, and low-impact activities like swimming or cycling. For those recovering from injury or dealing with chronic conditions like arthritis, physical therapy can be particularly beneficial.
Medications & Injections
Medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be helpful in managing the pain and inflammation associated with back of knee pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger anti-inflammatory medications or recommend corticosteroid injections for more significant relief. These treatments can be an essential part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
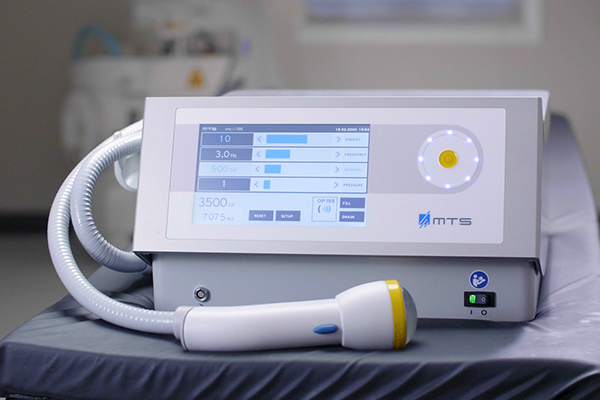
SoftWave Therapy
SoftWave therapy is an advanced shockwave therapy for knee pain. This non-invasive treatment uses broad-focused, low-intensity parallel shockwaves to effectively address back of knee pain. Utilizing a parabolic reflector applicator, these shockwaves penetrate both superficial and deep tissues, triggering a biological response that initiates healing. This innovative therapy modulates inflammation, increases blood flow, promotes angiogenesis, and stimulates the release of cytokines and growth factors, making it particularly effective for reducing both acute and chronic pain.
The key advantages of SoftWave therapy include its deep tissue penetration, which enhances its biological effects, and its ability to treat complex cases of back of knee pain without the need for surgery or analgesics. Patients benefit from shorter treatment times, quicker recovery periods, and a non-invasive approach that is well-tolerated, making it an appealing choice for those seeking to relieve pain and restore mobility efficiently.
Surgical Options for Persistent Back of Knee Pain
In cases where non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be necessary. Surgery is typically considered for severe injuries, such as torn ligaments, meniscus tears, or advanced arthritis that doesn’t respond to other treatments. Common surgical procedures for back of knee pain include arthroscopy, where a small camera is inserted into the knee joint to repair damaged tissues, and knee replacement surgery for more severe cases.
Recovery from knee surgery varies depending on the procedure, but it often involves a period of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activities. While surgery can be effective, it’s generally reserved for cases where other treatments have not been successful.
Preventing Back of Knee Pain: Tips and Best Practices
Preventing back of knee pain involves adopting healthy habits and taking proactive steps to protect your knee health. Here are some tips to help you avoid knee pain in the future:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Carrying excess weight can put added stress on your knees, increasing the risk of pain and injury. Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce this strain and protects your joints.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps keep the muscles around your knees strong and flexible. Engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling is gentle on the knees while providing a good workout.
- Wear Supportive Footwear: The shoes you wear can significantly impact your knee health. Choose footwear that offers adequate support and cushioning, especially if you spend a lot of time on your feet.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain in your knees, and don’t ignore them. If you notice persistent pain,
The Best Shockwave Therapy for Back of Knee Pain
Are you looking for safe, reliable, and effective relief from back of knee pain?
SoftWave therapy is FDA-cleared, patented, and nationally recognized for its leading tissue regeneration technology. Unlike other types of high-energy shockwave treatments, SoftWave is the only shockwave therapy on the market that uses true broad-focused shock waves that treat larger and deeper areas of tissue.
Thousands of patients have experienced the benefits of SoftWave for knee pain, including:
- Little to no side effects
- Short treatment time
- Quick recovery
- Long-lasting results
Find a SoftWave Therapy provider near you or learn more about SoftWave and whether or not you’re eligible for full treatment today!
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The content provided in this blog should not be used to diagnose or treat any health problems or illnesses. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your healthcare routine or treatment plan.
New Patient Special
Try SoftWave for just $69 at a clinic near you and learn if you’re a candidate for full treatment